Earlier this month I wrote a post showing that higher education enrolments at age 19 years, and the domestic participation rate at age 19, were down in 2023 compared to 2022.
This post explores possible reasons for this downward trend.
The teenage job market
One explanation of declining enrolments at age 19 is higher education’s counter-cyclical relationship with the labour market. At the margins, some people prefer work to study, but study when work is not available. The higher education participation and full-time employment rates in the chart below match this theory. Higher education participation increased after COVID-related full-time job losses in 2020 and then decreased as job opportunities returned.
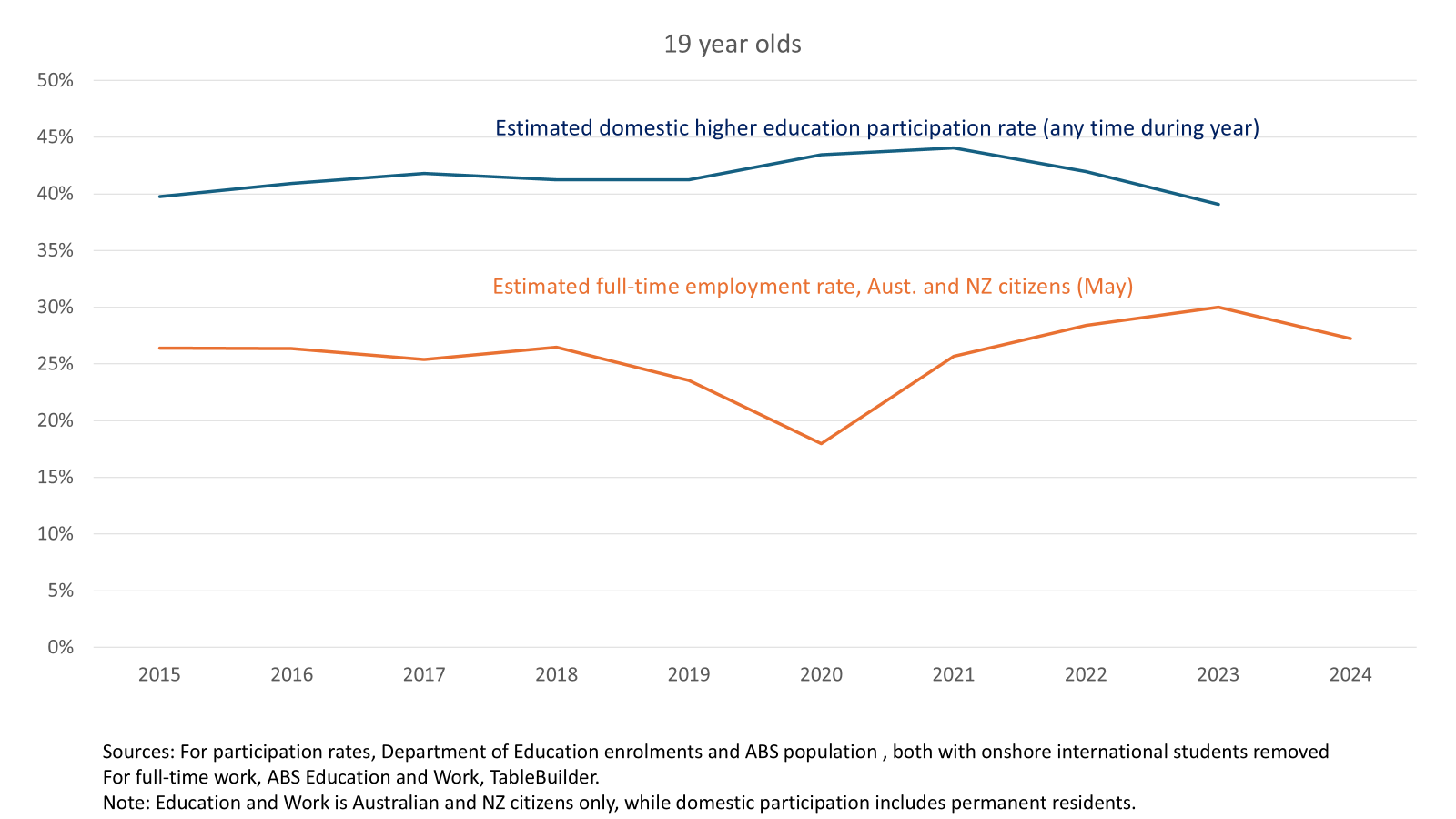
Education and Work TableBuilder supports analysis of smaller sub-groups than the standard ABS data releases, but with an increased risk of rogue results. Broader 15-19 year old statistics, however, confirm 2023 as a very strong year for full-time teenage employment. Both sources show that teenage full-time jobs grew strongly post-COVID and then softened in 2024, while remaining good compared to the 2010s.
Read More »