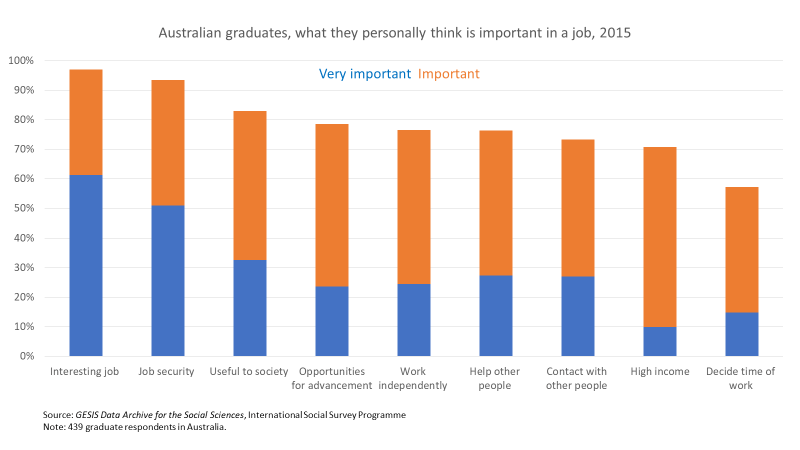
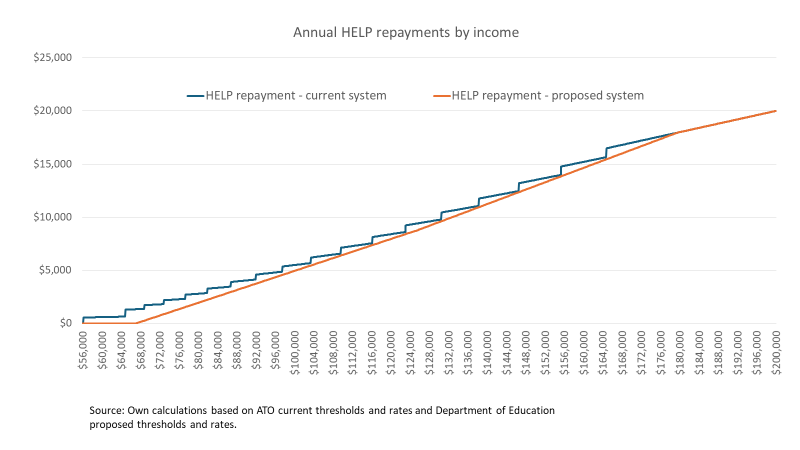
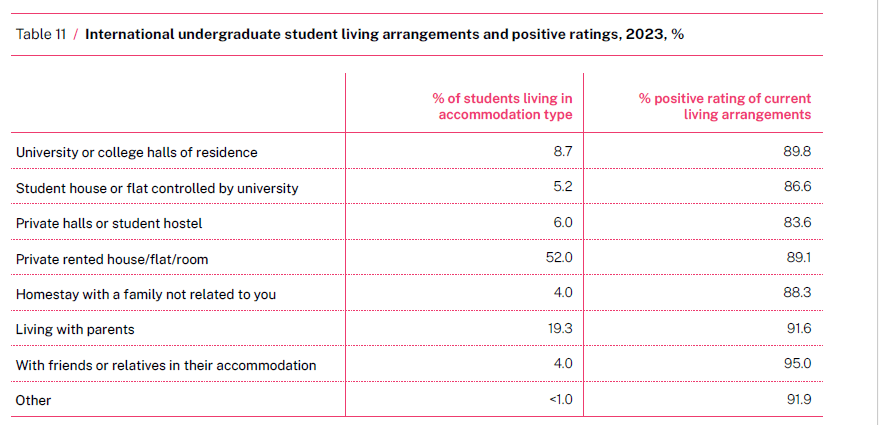
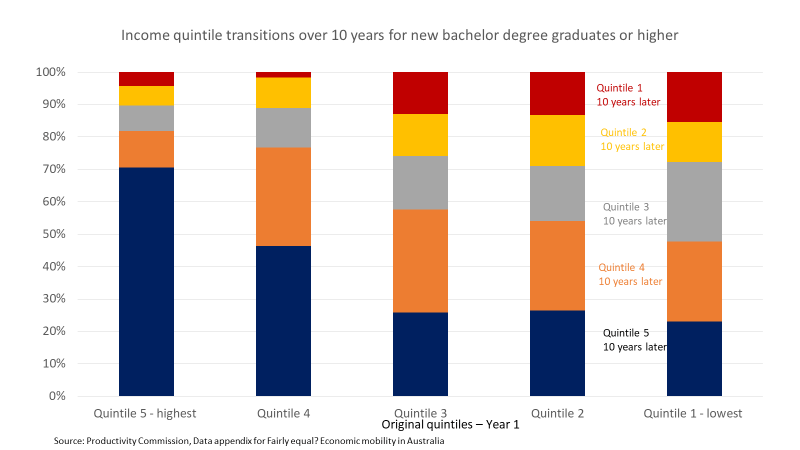With universities back job shedding, academics and their unions are looking for someone to blame. University leaders and consultants are being attacked for poor decisions. The government also gets criticised. UTS history professor Anna Clark says that over the last twenty years ‘we have seen gradual, steady decline in government investment across the sector’. In his recent lament Broken Universities, Graeme Turner says that there has been a ‘steady decline in the levels of funding per student’.
Five years ago, early in the COVID crisis, I wrote a post about government ‘cuts’. This post is an update.
Funding for Commonwealth supported students
As my earlier post noted, time series data is not straightforward. The chart below focuses on the major student funding programs, in today’s terms the Commonwealth Grant Scheme (CGS), HECS-HELP, and upfront student contributions. These funding sources have always had a link to the number of full-time equivalent Commonwealth supported students, although historically the money they delivered supported research as well as teaching expenditure.
Around these core funding sources other schemes serve the same purpose (e.g. transition funding) or similar purposes (e.g. NPILF). The chart below includes the Job-ready Graduates (JRG) transition funding and but excludes NPILF. It includes money paid from the Higher Education Continuity Guarantee, a COVID measure still in place for universities that ‘under-enrol’ that would normally face a CGS penalty. From 2021-2024 the time series excludes the enabling course loading that was previously in the CGS but moved to IRLSAF. But this funding is back in the CGS in 2025 due to the FEE-FREE Uni Ready places. The regional loading remains out from 2021 as it is still in IRLSAF and will join needs-based funding next year.
Overall my time series goes for simplicity over a full count of expenditure on student-related programs. In the time series, one big structural change should be noted, which is research student funding moving to a separate program from 2001, which caused a significant but artificial year-on-year decline.
Trends in total funding
Focusing on recent times, in nominal dollar terms total CGS funding dipped between 2021 and 2022, which was mostly short-term COVID places coming out of the system. HECS-HELP lending fell between 2020 and 2021, driven by the strange decision to pass on reduced JRG student contribution rates to all current students but to grandfather increased student contribution rates, so that only 2021 and later commencing students pay them. HECS-HELP lending fell again in 2022, with lower student numbers also affecting revenue from a university perspective.