Yesterday the government introduced legislation to extend demand driven funding from regional and remote to all Indigenous students. Currently Indigenous students from major cities are funded from within each university’s capped maximum basic grant amount for higher education courses. If the legislation passes universities will get the full Commonwealth contribution value of all enrolled Indigenous students in demand driven funding eligible courses, with no funding cap.
What are current Indigenous enrolments by geographic category?
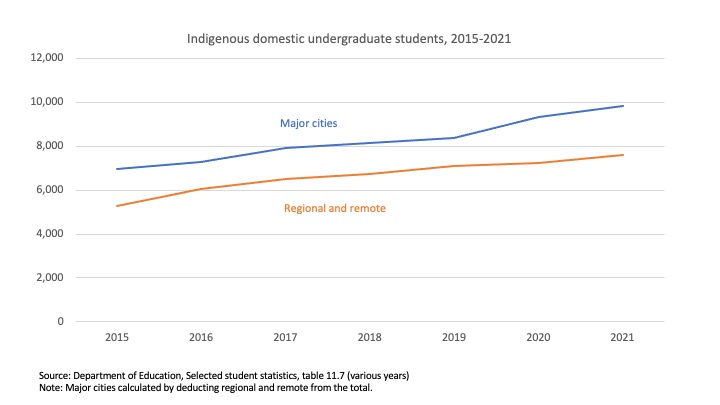
Demand driven funding only applies to bachelor degree students – of which more later – which makes it a funding category that is not also a publicly-reported statistics category. However a table in the annual equity statistics lets us calculate the number of undergraduate (ie bachelor + diploma + associate degree) Indigenous students by home geographic location. It shows that Indigenous students from the major cities outnumber regional and remote students. Enrolments from both groups have increased in recent years.